OBD-II, short for On-Board Diagnostics II, is the built-in system vehicles use to monitor engine operation and emissions while the car is running. It tracks performance continuously, rather than only during inspections or repairs.
Data from sensors across the engine and exhaust systems is sent to the vehicle’s control computer and evaluated in real time. When something falls outside normal operating limits, the system logs a diagnostic trouble code that points to the affected area.
That information can be accessed through a standardized 16-pin diagnostic port found in most vehicles built since the mid-1990s. Because the interface and data format are universal, the same diagnostic tools work across different manufacturers.
How Does OBDII Work in a Vehicle?
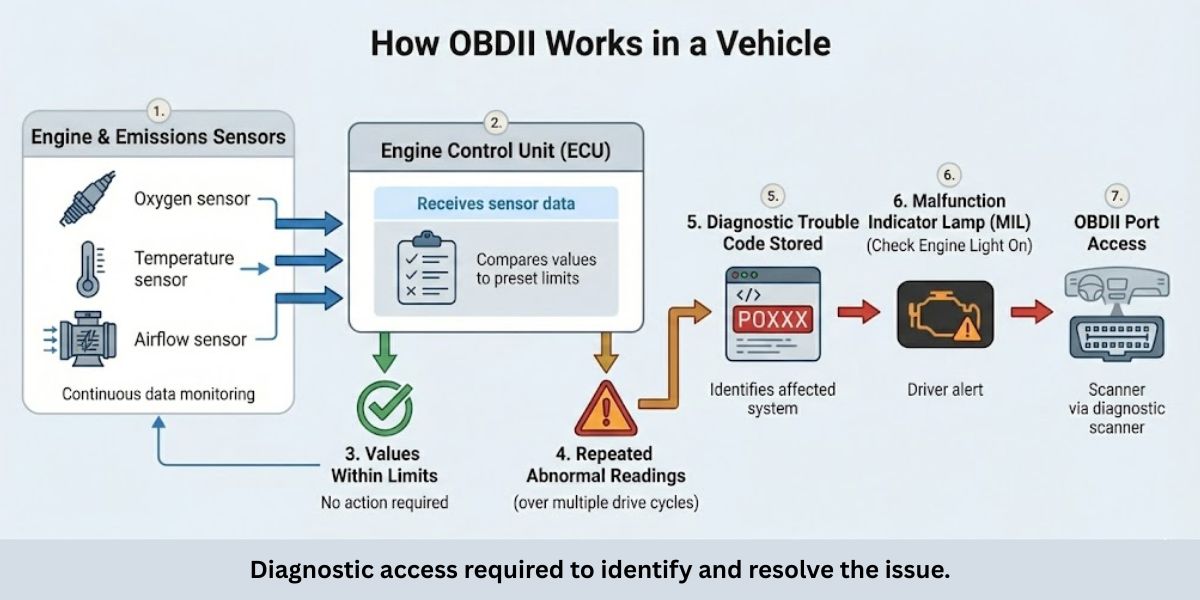
OBDII works by checking whether the engine and emissions systems are operating within defined limits while the vehicle is running. Sensors send data to the engine control unit, which continuously compares those values against expected standards.
If a reading repeatedly falls outside those limits, the system recognizes it as a fault rather than normal variation. OBDII then records the issue as a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that identifies the system where the problem occurred.
When a stored fault affects emissions or engine performance, the system turns on the Check Engine Light to alert the driver. That warning simply indicates that a code has been saved and diagnostic access through the OBDII port is required.
What Information Does the OBDII System Provide?
OBDII exposes diagnostic and operating data that shows faults, operating conditions, and system status.
- Trouble Codes: When a fault is confirmed, OBDII stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that identifies the system operating outside defined limits.
- Freeze Frame: At the time the code is stored, the system saves a snapshot of key operating values such as speed, temperature, and load.
- Live Data: Current sensor readings remain available, allowing present behavior to be compared against the stored fault conditions.
- Readiness Status: Emissions-related self-tests are tracked to indicate whether required monitors have completed successfully.
What Is an OBDII Port and Where Is It Located?
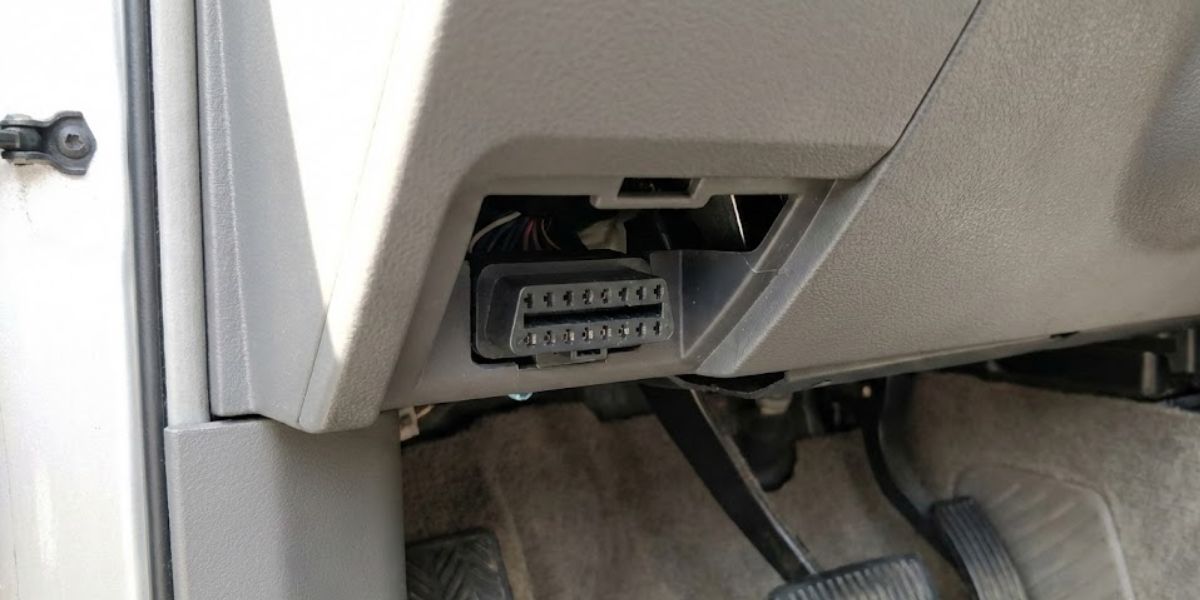

The OBDII port connects diagnostic tools directly to the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. Through this connection, trouble codes, live data, and system status information become accessible.
A universal 16-pin connector, defined by the SAE J1962 standard, is used for this port across manufacturers. That standardization allows the same OBDII scanner to work on most vehicles without special adapters.
Placement is typically under the dashboard near the steering wheel, where the port can be reached easily. Accessibility is required by regulation, ensuring the port remains visible and usable regardless of vehicle brand.
What Is an OBDII Scanner and How Is It Used?
An OBDII scanner is a device that plugs into the OBDII port to read data stored by the vehicle’s diagnostic system. It provides access to trouble codes, live sensor data, and emissions status information.
Once connected, the scanner communicates with the vehicle’s control unit and retrieves diagnostic trouble codes recorded during operation. These codes help identify which system reported a fault and guide further inspection or repair.
Many scanners also display real-time data, allowing current engine and system behavior to be observed while the vehicle is running. This makes the scanner useful not only for diagnosing problems but also for confirming whether an issue has been resolved.
What Are OBDII Codes?
OBDII codes are standardized fault codes generated when the vehicle detects abnormal operation in a monitored system. Each code represents a specific type of issue rather than a failed part.
The code format identifies the system involved, such as the engine, transmission, or emissions controls, and whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific. This structure allows the issue to be categorized consistently across vehicles.
OBDII codes are used to guide diagnosis by narrowing the problem area. They indicate where to begin testing, not what component must be replaced.
What Are Common OBDII Trouble Codes?
Common OBDII trouble codes are grouped by how the powertrain control system classifies faults across the engine, transmission, and emissions systems.
- Generic Powertrain Codes (P0xxx): These codes are defined by the OBDII standard and appear across all vehicle brands, usually pointing to engine operation, fuel control, or transmission-related issues.
- Manufacturer-Specific Codes (P1xxx): Vehicle manufacturers use these codes to report faults tied to their own engine designs, control strategies, or proprietary components.
- Emissions-Related Codes: Many OBDII codes focus on emissions control systems such as oxygen sensors, catalytic converters, and evaporative emissions components, since these directly affect regulatory compliance.
- Misfire Codes (P0300–P030X): These codes indicate combustion problems in one or more cylinders and are closely monitored because of their impact on engine performance and emissions output.
- Sensor and Circuit Codes: Faults involving sensors or electrical circuits appear when signal values fall outside expected ranges or fail to respond correctly, often influencing multiple systems at once.
Why Is OBDII Important for Vehicle Maintenance and Emissions?
OBDII is important because it connects vehicle maintenance decisions directly to measured engine and emissions performance.
Early Fault Detection
OBDII identifies abnormal system behavior before symptoms become obvious to the driver. This allows maintenance to be based on recorded faults rather than delayed reactions to breakdowns.
Accurate Diagnostics
The system provides standardized diagnostic trouble codes and supporting data that narrow problems to specific systems. This reduces unnecessary part replacement and shortens repair time.
Emissions Monitoring
OBDII continuously checks components that affect exhaust emissions, including fuel control and after-treatment systems. Faults that increase emissions are detected and logged automatically.
Regulatory Compliance
Emissions readiness data from OBDII is used during vehicle inspections to confirm compliance with environmental standards. A vehicle cannot pass inspection if required monitors are incomplete or faults remain active.
What to Look for When Using an OBDII Scanner
An OBDII scanner should make it clear what the vehicle is reporting and whether the issue is active, resolved, or recurring.
Code Access
The OBDII scanner must reliably read and clear diagnostic trouble codes without delay. If codes cannot be retrieved consistently, the tool has limited value.
Live Data Visibility
Access to live sensor data shows how the engine and emissions systems are behaving in real time. This helps confirm whether a stored fault is still present.
Readiness Information
Readiness status indicates whether emissions-related systems have completed required self-tests. This is essential for inspections and post-repair verification.
Ease of Use
The interface should present codes and data clearly without forcing interpretation through menus or abbreviations. A scanner that slows understanding defeats its purpose.
OBD vs. OBDII: Key Differences
| Feature | OBDI | OBDII |
| Standardization | Manufacturer-specific | Industry-standard |
| Year Introduced | Early 1980s | 1996 |
| Connector Type | Varies | 16-pin universal |
| Code Format | Non-standard codes | Generic and manufacturer DTCs |
| Diagnostic Access | Limited | Extensive |
OBDII replaced OBDI for its broader compatibility, standardized connectors, and real-time monitoring.
OBD and Telematics
OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) and telematics work together to provide real-time insights into a vehicle’s mechanical condition and usage patterns. Telematics systems use data from the OBDII port to monitor how the vehicle is driven and how well it’s performing internally.
Key functions supported by OBD-powered telematics:
- Live engine diagnostics: reads fault codes and performance data while the vehicle is in use
- Fuel usage tracking: monitors real-time fuel consumption to spot inefficiencies
- Idle time analysis: identifies unnecessary engine run time to reduce wear and fuel waste
- Maintenance alerts: sends automated reminders based on engine hours or usage patterns
- Driver behavior reports: tracks patterns like harsh braking or rapid acceleration for performance reviews
Combining OBD with telematics improves maintenance accuracy, reduces downtime, and helps operators and owners make smarter decisions based on real usage data.
Take Control of Your Fleet in Seconds with Matrack OBD Plug-In Tracker

Matrack OBD Plug-In Fleet Tracker connects directly to a vehicle’s OBDII port and starts working right away, no tools or wiring needed. It’s a quick solution for tracking both vehicle health and driver activity in real time.
This tracker helps monitor engine performance, fuel use, and idle time, giving clear data to reduce downtime and avoid costly repairs. It also captures key behaviors like harsh braking and speeding to improve driver safety.
You can access everything through Matrack’s simple dashboard and mobile app, making it easy to manage your fleet from anywhere. The plug-in design makes it perfect for fleets that need fast setup and reliable tracking.


